Seasonal winds & Local winds
Planetary winds
- Blows at global level.
- Blows throughout the year.
- Example - Trade winds, Westerlies, Polar Easterlies
Seasonal winds
- They are smaller in scale.
- Blows not all throughout the year.
- Blows in a particular season (in particular direction).
- Example - Indian monsoon
Local winds
- They are very smaller in nature.
- Blows due to local differences in heating of Earth's surface.
- Example - Loo, Chinook, Land breeze and Sea breeze, etc.
Seasonal winds - The seasonal difference in temperature and pressure condition cause the movement of air and subsequent winds blowing in a particular seasons are known as Seasonal winds.
Example - South west monsoon of South Asia.
Local winds - Differences in heating and cooling of Earth's surface and the cycles those developed daily or annually can create several common winds called local or regional winds.
Example - Loo, Chinook, Land breeze and Sea breeze, etc
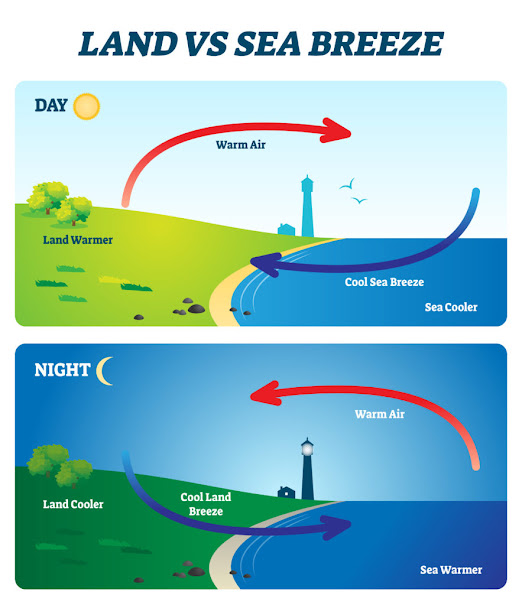
Land breeze and Sea breeze
- Near to the coastal regions, the land gets heated more quickly than the adjacent sea during the day time.
- This creates a relatively low pressure over the land and relatively high pressure over the adjacent sea.
- This cause the circulation of relatively cooler air from sea to the adjacent land which is known as Sea breeze which blows in the late afternoon and evening.
- The rapid loss of heat from the land causes the reversal of daytime pressure condition leading to relatively high pressure on land and relatively low pressure over the ocean during night.
- Winds blow from land to sea which is known as Land breeze which blows at late night and early morning.
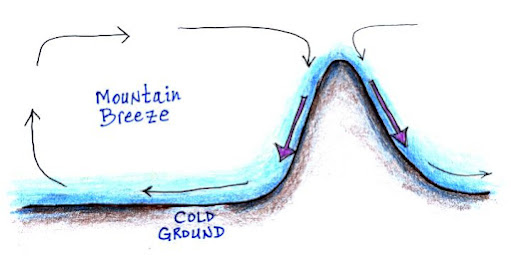
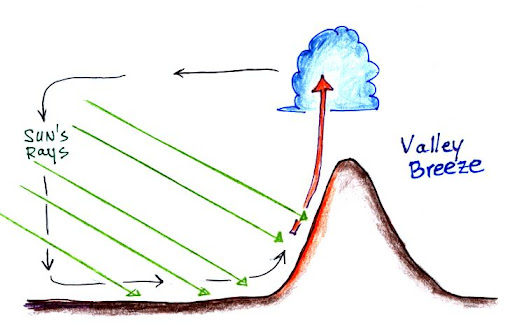
Mountain and Valley breeze
- During the daytime, the mountain slopes heat up rapidly as compared to the valley resulting in air from the valley moving up along the slopes which is known as Valley breeze.
- At night, the temperature difference between the mountain slopes and valley is reversed causing the winds to blow from mountain to the valley which is known as Mountain breeze.
- Valley breeze is also known as Anabatic breeze while Mountain breeze is also known as Katabatic breeze.
Mountain slopes - more exposed → loses heat faster than the valley side → High pressure is created at mountain slopes → very cold winds blow from mountain slopes to valley sides
Mountains being more exposed to sunlight → gets heated more than the valley side → low pressure is created at the mountain slopes → winds blow from valley side to mountain slopes
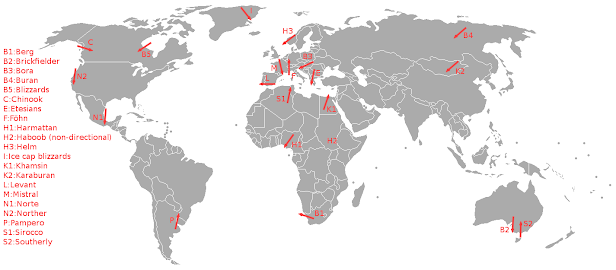
Other important local winds -
1. Chinook
- Hot and dry local winds of North America
- It blows along the eastern slopes of Rockies mountains.
- It is also known as Snow eater as when it descends and came to snow covered prairies, it melts the snow cover and made the grassland snow free.
- Direction - West to East
2. Foehn
- Hot and dry winds of Europe
- It blows along the northern slopes of Alps.
- Affects Switzerland the most.
- Direction - ↙↙
3. Harmattan
- Hot and dry winds of Africa
- It blows from North-east and East to South-west and West.
- It affects Nigeria the most.
- It is also known as Doctor of Guinea coast.
4. Haboob
- Hot and dry winds of Africa.
- It affects Sudan the most.
5. Sirocco
- Hot and dry wind of Africa
- It blows from Sahara to Mediterranean sea.
- It causes Blood rain in Italy, Spain and surrounding area as it brought reddish sand from Sahara and when it passes over the Mediterranean sea it pick up moisture leading to blood rain.
- There are different names of Sirocco in different parts of the world.
- It is known as Khamsin in Egypt, Gibli in Libya, Chili in Tunisia, Leveche in Spain & Canry and Leste in Madeira islands.
6. Berg
- Hot and dry wind of South Africa
7. Kara Buran
- Hot and dry wind of Mongolia and North China
8. Brick fielder
- Hot and dry wind of Australia
9. Loo
- Hot and dry wind of North India
10. Blizzard
- Cold winds of Canada and USA
11. Buran
- Cold winds of Russia
12. Norte/Norther
- Cold winds of North America (South USA & Mexico)
13. Pampero
- Cold winds of South America
- It is named after the temperate grassland of Argentina (Pampas)
14. Mistral
- Cold winds of France and Spain
15. Levant
- Cold winds of South Spain
16. Bora
- Cold winds blowing along the coast of Itlay
17. Southerly
Previous Article - Planetary winds
Next Article - Humidity, Evaporation & Condensation
Notes on other subjects
Optional Notes
Note - This is my Vision IAS Notes (Vision IAS Class Notes) and Ashutosh Pandey Sir's Public Administration Class notes. I've also added some of the information on my own.
Hope! It will help you to achieve your dream of getting selected in Civil Services Examination 👍




0 Comments