Rocks & Types of Rocks
Rocks - Any naturally occurring agglomeration of mineral particles forms rocks.
Difference between Rocks and Minerals -
Rocks -
- Rocks are aggregates of mineral elements.
- A rock has no definite chemical composition.
- Minerals are organised to form rocks.
- The three chief types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks.
- Example - Basalt, Granite, Slate, Marble, etc
Minerals
- Minerals are solid inorganic substances occurring naturally.
- Minerals have definite chemical composition.
- Elements are organised to form compounds which are minerals.
- Four chief mineral groups are - Silicates, Carbonates, Sulphides and Metallic minerals
- Example - Iron, Silicon, Nickel, etc
Types of Rocks
Igneous Rocks - These are the rocks formed due to cooling, solidification and crystallization of molten materials of the Earth.
These are of two types -
- Intrusive igneous rocks (Plutonic rocks) - These are formed from magma cooled inside the Earth or below the Earth's surface. Examples - Granite, Diorite, Gabbro, etc
- Extrusive igneous rocks (Volcanic rocks) - they are formed from cooling of magma (lava) above the Earth's surface. Example - Basalt, Andesite, stc
It can also be classified on the basis of Silica content.
- Basic (Mafic) - with Silica content < 52%
Example - Basalt, Gabbro
- Acidic (Felsic/Silcis) - with Silica content> 66%
Example - Granite
Igneous rocks don't contain any fossils and don not have any layers or strata (like sedimentary rocks).
Igneous rocks are also called Primary Rocks as they are directly formed from the magma.
Sedimentary Rocks - These are the secondary rocks formed by the solidification of sediments derived from original igneous rocks or another sedimentary rocks or metamorphic rocks.
Example - Sandstone, Limestone, Chalk, Clay, Coal, Gypsum, etc
Stages in the formation of Sedimentary rocks.
- Weathering - which involves the breaking up of original rocks into sediments.
- Transportation by different agents such as wind, water, gravity, etc.
- Deposition into a basin
- Lithification - which is the conversion of lose sediments into hard rocks
- Compaction - where the sediments are squeezed by the weight of over lying layers
- Cementation - which involve the binding together of compacted sediments and filling up of the pore spaces by natural materials.
Sedimentary rocks contain different layers or strata and they also contain rich fossil evidences.
Types of Sedimentary Rocks -
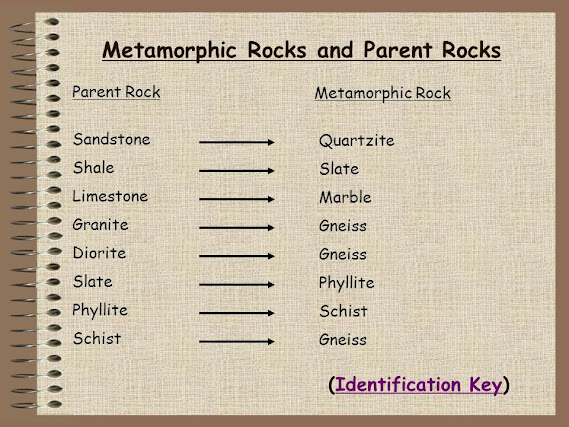
Metamorphic Rocks - They are the rocks produced due to changes through physical or chemical processes. The change in pressure condition results in 'dynamic metamorphism' and the change in temperature leads to 'thermal metamorphism' and in case of change of both temperature and pressure, it is called 'thermo-dynamic metamorphism'.
Example - Marble, Slate, Schist, Gneiss, etc
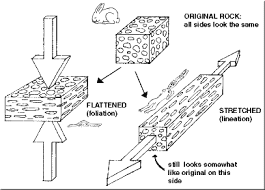
Foliation and Lineation are the processes involved in metamorphism.
Foliation - When minerals are arranged in a series of band in a plane, it is called foliation.
Lineation - When minerals are arranged in linear manner, it is called lineation.
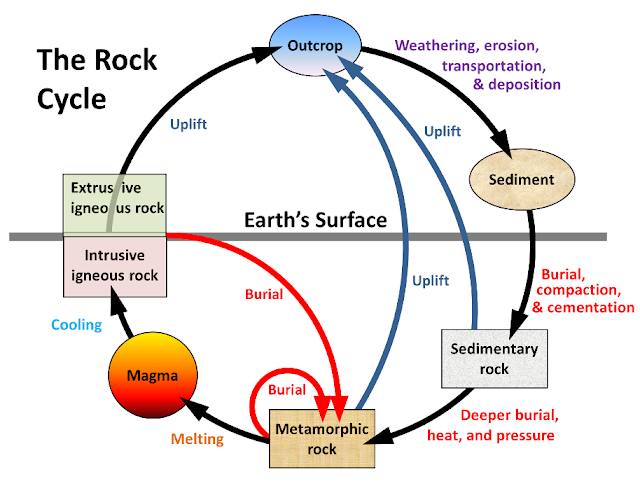
Rock Cycle
Rock cycle - Conversion of one rock to another and then to another is known as rock cycle.
Previous Article - Interior of the Earth
Next Article - Earth's Movement
Notes on other subjects
Optional Notes
Note - This is my Vision IAS Notes (Vision IAS Class Notes) and Ashutosh Pandey Sir's Public Administration Class notes. I've also added some of the information on my own.
Hope! It will help you to achieve your dream of getting selected in Civil Services Examination 👍








0 Comments